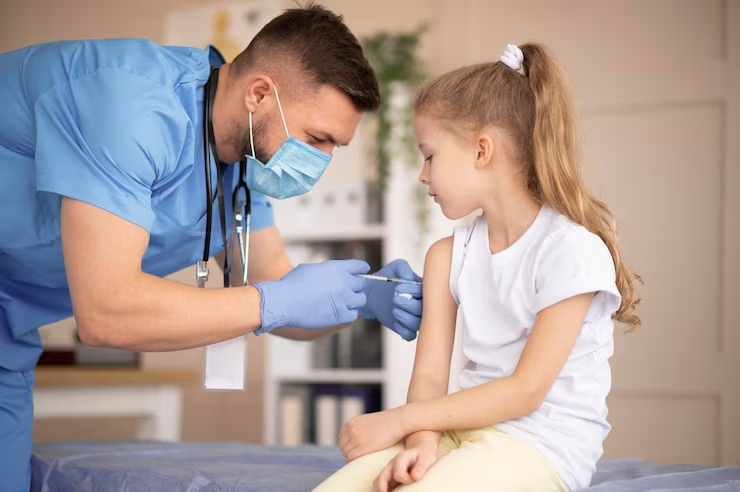
Recognizing that financial constraints could pose a barrier to healthcare access, Dr. Emily collaborated with local philanthropists and international aid organisations to secure funding for subsidised or free vaccinations. She emphasised that the health of the rural areas residents’ children should never be compromised due to financial limitations and worked tirelessly to ensure that cost would not be a hindrance to receiving essential vaccines.
Doctors of Best hospitals in Pakistan also stressed the significance of community engagement and collective responsibility.To raise understanding and invalidate preconceptions about vaccinations, she urged individuals from the community to volunteer as ambassadors for immunisation beyond the communities they belong to. She did this through promoting an atmosphere in which everyone takes personal and communal responsibility for their physical and mental wellness.
Additionally, Dr. Emily recognized the importance of engaging with rural area residents on a personal level. She organised community meetings and conducted house visits, listening to the concerns and addressing the specific health needs of each family. Through these interactions, she encouraged the residents to prioritise their health and the health of their children, emphasising that investing in preventive measures would lead to long-term benefits for the entire community.
Understanding the challenges faced by rural communities in accessing healthcare, Dr. Emily collaborated with local authorities and healthcare organisations to establish mobile vaccination clinics. These clinics travelled to remote areas, reaching out to families who were unable to visit the village health centre. By bringing vaccines directly to their doorstep, Dr. Emily ensured that no child was left unvaccinated due to geographical barriers or limited transportation options.
By manufacturing vaccines locally, the village community gained independence from unreliable supply chains and ensured a steady and sustainable provision of life-saving immunizations.
Dr. Emily understood the importance of addressing misconceptions and fears surrounding vaccines. She launched comprehensive education and awareness campaigns, engaging with parents, community leaders, and healthcare workers. Through these initiatives, she dispelled myths, shared scientific evidence, and fostered trust in the life-saving benefits of vaccines. Dr. Emily’s empathetic approach and ability to communicate complex medical information in simple terms resonated with the community, empowering them to make informed decisions about their children’s health.
As news of Dr. Emily’s groundbreaking efforts spread, neighbouring villages expressed interest in replicating her model. Recognizing the potential for widespread impact, Dr. Emily collaborated with like-minded individuals, creating a network of vaccine manufacturing hubs in underdeveloped areas. This collaborative approach not only empowered local communities to take charge of their healthcare but also strengthened the collective capacity to combat diseases on a regional scale.
The once burdened healthcare system in these villages underwent a remarkable transformation, ensuring a healthier future for generations to come.
Dr. Emily’s innovative model also had broader implications beyond vaccines. The establishment of local manufacturing facilities encouraged economic growth, creating employment opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship within the community. The newfound expertise in medicines of the best hospital in Multan further positioned the villages as regional leaders in healthcare, attracting investment and collaboration from international organisations.
Dr. Emily’s vision and unwavering commitment to revolutionising medicine manufacturing had ushered in a new era of healthcare in underdeveloped village communities.
Revolutionising Vaccine Technology:
Traditional vaccine production methods have relied on weakened or inactivated forms of pathogens, which can be time-consuming and complex. However, recent breakthroughs have introduced new vaccine technologies that offer alternative approaches with remarkable advantages.
MRNA Vaccines:
One notable advancement is the emergence of mRNA vaccines. This revolutionary technology employs genetic instructions encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) to stimulate the immune system against specific diseases. mRNA vaccines have gained significant attention due to their remarkable effectiveness against infectious diseases like COVID-19, as seen in the successful development of vaccines by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna.
Viral Vector Vaccines:
Viral vector vaccines are another groundbreaking development. They utilise harmless viruses as delivery vehicles to carry genetic material into human cells, triggering an immune response. These vaccines have shown promise in combating diseases like Ebola, and they offer the potential for rapid vaccine development against emerging pathogens.
Enhanced Protection:
The development of more effective vaccines using advanced technologies holds the promise of better protection against a wide range of diseases. mRNA and viral vector vaccines have demonstrated higher efficacy rates and the potential for broader immune responses compared to traditional vaccines.
Rapid Response to Pandemics:
One of the most significant advantages of these new technologies is their potential to expedite vaccine development during epidemics or outbreaks. With their modular nature, mRNA and viral vector platforms can be adapted and scaled up rapidly to address emerging threats. This agility is crucial in controlling the spread of infectious diseases and saving lives.
Global Vaccine Access:
The accessibility and equitable distribution of vaccines worldwide are critical for combating global health challenges. The advancements in vaccine technology can potentially facilitate large-scale production and streamlined distribution, aiding in addressing disparities in vaccine access between different regions and populations.
Future Disease Prevention:
The development of novel vaccine technologies opens doors to broader disease prevention strategies. By understanding the mechanisms behind mRNA and viral vector vaccines, scientists can explore their applications in preventing a wide range of infectious and non-infectious diseases, potentially revolutionising healthcare in the years to come.